Gartner’s latest research highlights that employee experience is now a primary focus for HR departments across various industries. This significant shift in focus emphasizes the increasing importance of creating a positive and engaging work environment for employees.
This shift underscores the need for CHROs (Chief Human Resource Officers) to integrate automation in a way that enhances, rather than detracts from, the employee experience. By carefully implementing automation tools and technologies, CHROs can streamline processes while maintaining a human touch that is essential for employee satisfaction and engagement.
In another comprehensive report by Gartner, they share four key automation enablers that CHROs can focus on to improve the overall employee experience (EX). These enablers are designed to help HR leaders make informed decisions about which processes to automate, ensuring that the automation efforts align with the goal of enhancing the employee experience. They suggest taking a human-centric approach when deciding which processes to automate, prioritizing the needs and well-being of employees throughout the automation journey.
In this detailed blog post, we’ll discuss those four automation enablers in depth and explore how CHROs can strategically balance the implementation of automation with its impact on employee experience. By understanding and leveraging these enablers, HR leaders can create a more efficient, yet empathetic, workplace that fosters both productivity and employee satisfaction.
Let’s look at each automation enabler.
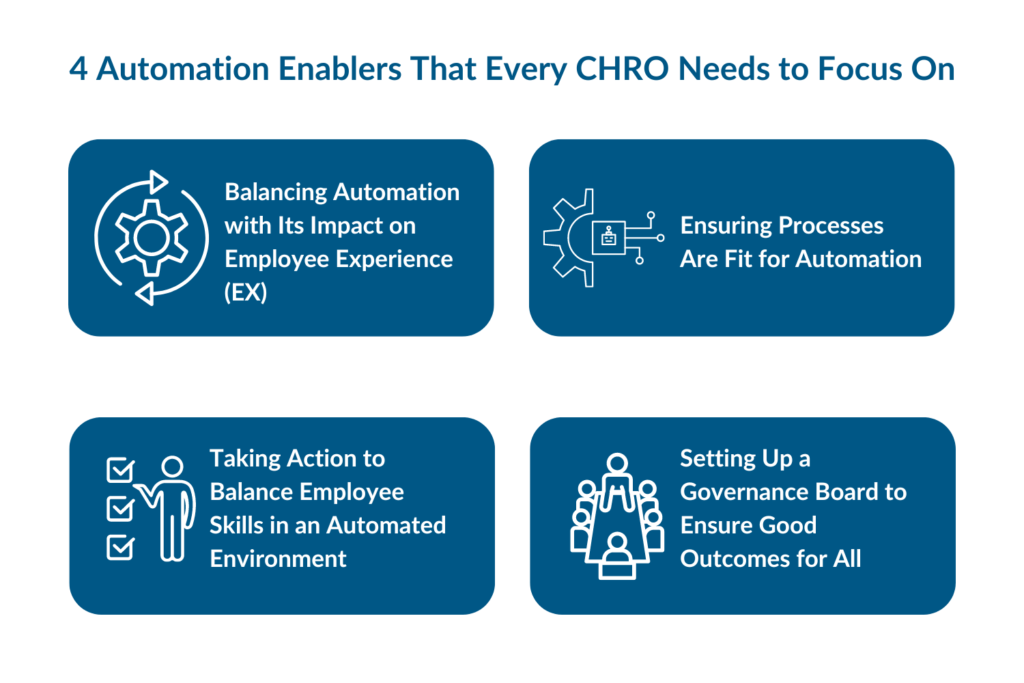
Balancing Automation with Its Impact on Employee Experience (EX)
Employee experience (EX) is a broad term that covers all the various interactions and experiences an employee has with their organization. This starts from the moment of recruitment and continues through the onboarding process, the day-to-day dealings with colleagues and superiors, and finally, offboarding. The importance of positive EX cannot be overstated. It plays a fundamental role in boosting employee engagement, improving retention rates, and enhancing overall productivity, thereby contributing to the success of the organization.
Automation has the potential to significantly amplify the EX, leading to a more engaged and satisfied workforce. By streamlining repetitive tasks and reducing the administrative load, automation not only speeds up processes but also allows employees to dedicate more of their time to meaningful, high-value work. This shift in focus can lead to improved job satisfaction and increased productivity.
For instance:
- Onboarding: The use of automation in onboarding processes can transform the experience for new hires. By digitalizing paperwork and automating training schedules, the process becomes seamless and engaging. As a result, new employees can integrate more rapidly and efficiently into the organization, setting the stage for a positive working relationship.
- Self-Service Portals: Automation tools in the realm of Human Resources, such as self-service portals, put power back into the hands of employees. These portals allow employees to access and manage their personal information, including leave requests and benefits enrollment, without needing to engage HR. This autonomy not only saves time for both employees and HR but also leads to a more empowered, engaged workforce.
Potential Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Automation, while it has the potential to significantly enhance the Employee Experience (EX), also presents a series of potential pitfalls that Chief Human Resources Officers (CHROs) must carefully navigate:
- Loss of Personal Touch: One of the main risks of an over-reliance on automation is the potential loss of personal interaction. This can often lead to a perceived lack of human touch, which in turn can have a negative impact on the overall EX. To mitigate this risk, CHROs should ensure that automated processes are designed in a way that they still include human touchpoints where necessary, preserving the personal feel and ensuring that employees don’t feel like they’re simply interacting with a machine.
- Change Management: Another key concern when implementing new automation tools is the potential disruption they can cause. This change can be unsettling for employees and if not managed properly, could lead to resistance and low adoption rates. To ensure a smooth transition, effective change management strategies need to be in place. These should include clear and regular communication about the changes, comprehensive training to help employees understand and adapt to the new technologies, and ongoing support to address any issues or concerns that may arise during the transition period.
Ensuring Processes Are Fit for Automation
While the advent of technology has offered numerous opportunities for automation, it’s crucial to acknowledge that not all human resources (HR) processes are suitable for this change. Chief Human Resources Officers (CHROs) need to conduct a meticulous assessment to identify which tasks can be automated without compromising the quality of output or the level of employee satisfaction. There are several key considerations to keep in mind during this process.
Firstly, repetitiveness. Tasks that are repetitive and time-consuming can tremendously benefit from automation. By automating these tasks, HR professionals can save significant amounts of time and focus more on strategic aspects of their work. Payroll processing, a task that requires meticulous attention to detail and consumes a substantial amount of time, is a prime example of such tasks. Similarly, data entry, which is notorious for its repetitiveness, can be automated to reduce the margin of error and enhance efficiency.
Secondly, standardization. Processes that consistently follow a standardized workflow are more amenable to automation. These processes are less reliant on human judgment and can be carried out uniformly, making them ideal for automation. Conversely, tasks that require frequent human intervention, judgment, or customization may not be as suitable for automation as they often require a human touch to ensure effectiveness.
Tools for Process Assessment
CHROs have at their disposal a variety of tools and methodologies that can be utilized to determine the appropriateness of different processes for automation. These tools provide important insights to guide decision-making:
- First, Process Mapping serves as an effective tool. This involves the creation of visual representations of workflows, which can help pinpoint specific areas where automation can be implemented to the greatest effect. By visualizing the process, it becomes easier to identify bottlenecks or redundant steps that might be eliminated or streamlined through automation.
- Second, conducting a thorough ROI Analysis is crucial. This means evaluating the potential return on investment for automating a particular process. By doing this, it becomes easier to prioritize automation initiatives that offer the highest potential benefits. This ensures that resources are allocated in the most efficient way, focusing on areas where automation can deliver the greatest returns.
Implementing Automation in Phases
Adopting a phased approach to implementing Human Resources automation can lead to smoother transitions and better outcomes, ultimately driving efficiency within the department. It’s crucial for Chief Human Resources Officers (CHROs) to initiate this process by focusing first on tasks of lower complexity. These tasks could include basic administrative duties, such as tracking employee attendance or managing leave applications, or simple data entry tasks, like updating employee records or inputting new hire information.
By automating these simpler tasks initially, the HR department can ease into the transition, allowing employees to gradually become comfortable with the new systems and processes. Once these tasks are successfully automated and the team has adjusted to the changes, CHROs can then gradually progress to automating more complex processes.
These might encompass strategic tasks like talent management, where automation could streamline the process of identifying and nurturing potential leaders within the organization, or benefits administration, where automation could eliminate errors and ensure compliance with regulations. This step-by-step approach allows for a continuous feedback loop, providing regular opportunities to evaluate the effectiveness of the automation.
These checkpoints allow for necessary adjustments to be made, ensuring that the changes are positively impacting the efficiency of the HR department and aligning with the overall organizational goals. Through this iterative process, the organization is able to ensure that it is getting the most benefit from the automation process, maximizing return on investment, enhancing productivity and ultimately driving the organization towards its strategic objectives.
Taking Action to Balance Employee Skills in an Automated Environment
Automation, a transformative force in the modern world, is significantly reshaping the landscape of skills within an organization. The advent of technology has led to an automation revolution, which is changing the way we work and the skills we need. As certain tasks become increasingly automated, certain skills, which were once deemed essential, may become obsolete or less important. This is a natural consequence of the technological evolution, and it is something that organizations must prepare for.
On the other hand, new skills are emerging, particularly those that leverage the power of automation and artificial intelligence. These skills are becoming increasingly crucial in the current business ecosystem and will likely be in high demand in the future. This shift in the skills landscape presents a unique, unparalleled challenge to Chief Human Resources Officers (CHROs), who sit at the helm of managing this transition.
CHROs have an important role to play in this evolving landscape. They must proactively manage this transition, ensuring that their organization is prepared for the changes that automation brings. It is imperative that they carefully execute strategies to maintain a balanced workforce. This workforce should not only possess traditional skills but also be equipped with the new, technologically advanced skills required in the evolving business environment.
The goal of every CHRO should be to ensure their organization is well-equipped with a highly skilled workforce that is capable of adapting to the changes brought about by automation. They must strive to create a future-ready workforce, comprised of individuals who are versatile, adaptable, and prepared for any technological advancements. This is no small task, but it is a vital one for the success of any organization in the digital age.
Identifying Skill Gaps
To effectively balance the skills of employees and ensure the longevity and success of the organization, Chief Human Resource Officers (CHROs) need to take a proactive approach in identifying both current and future skill gaps. This involves two key strategies:
- Skill Audits: The implementation of regular skill audits is essential. This process involves a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of the collective skills within the organization. The audits help identify areas of strength and, more importantly, areas where employees may need further development, whether through upskilling – expanding their skill set within their current role, or reskilling – learning new skill sets for a different role. By conducting these audits, CHROs can ensure that their employees are always equipped with the necessary skills to meet their job demands.
- Future Skills Forecasting: Another crucial strategy is the anticipation of future skill requirements. This is based on the careful observation of emerging technologies and industry trends. By forecasting the skills that will be in demand in the future, CHROs can ensure that the organization is not only prepared for changes but can also stay ahead of the curve. This proactive approach to talent development ensures that the organization is always ready to adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
Strategies for Skill Development
Chief Human Resource Officers (CHROs) play a pivotal role in ensuring the workforce is adequately prepared and skilled for the evolving landscape of the future of work. They shoulder the responsibility of identifying the necessary skill sets and implementing strategies to foster these skills within their teams:
- Launching Upskilling and Reskilling Initiatives: A significant strategy that CHROs can adopt is the initiation of comprehensive upskilling and reskilling programs. These programs are meticulously designed to aid employees in acquiring new skills or refining their existing ones, an aspect that is of paramount importance in the dynamic and fast-paced business environment of today. The execution of this strategy can be accomplished through various methods, such as conducting regular in-house training sessions, providing access to relevant online courses, and forging strategic collaborations with external educational institutions to provide specialized training.
- Developing Individualized Career Development Plans: A second, no less important strategy is the creation of personalized career development plans for every employee. These individually tailored plans can assist employees in aligning their personal career aspirations and growth with the ever-evolving needs of the organization. This alignment ensures that they remain relevant, adaptable, and productive in a business environment that is increasingly embracing automation. The benefits of such an approach are twofold – it aids employee personal development and contributes to the overarching success and progress of the organization.
Setting Up a Governance Board to Ensure Good Outcomes for All
A governance board plays a crucial and indispensable role when it comes to guiding and overseeing the implementation of human resources automation initiatives within a business or organization. This esteemed authority acts as the guardian of the company’s strategic plans and ensures that the automation initiatives are carefully aligned with the broader organizational goals. It is their responsibility to make sure that these technological advancements not only serve the operational needs of the company but also adhere to the ethical standards that the organization firmly upholds.
Moreover, the governance board is pivotal in safeguarding the welfare and well-being of the organization’s employees during the implementation of these automation processes. They act as the protector of the workforce, making sure that their interests are not just considered but prioritized and protected throughout the transition to a more automated system.
In essence, the governance board serves as the bridge between the organization’s management and its employees, ensuring a balance between operational efficiency and employee satisfaction. They hold the responsibility of ensuring that the transition to automation is smooth and beneficial for all parties involved, thus playing a key role in the success of the organization’s automation initiatives.
Responsibilities of the Governance Board
The governance board is a critical element in the successful implementation of human resources automation efforts. Their role is multifaceted and should include clearly delineated responsibilities to ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of these efforts:
- Setting Objectives: One of the primary responsibilities of the board should be to define clear, measurable objectives for automation initiatives. These objectives should be aligned with the broader organizational goals. By doing so, the board can help ensure that any automation projects undertaken contribute significantly to the strategic objectives of the company, thereby maximizing the return on investment.
- Monitoring Progress: Consistent and systematic review of the progress of automation projects is another crucial responsibility of the governance board. Regular reviews and updates not only ensure that these projects stay on track and adhere to their timelines, but it also ensures that they ultimately meet their intended outcomes. This active monitoring helps to identify potential issues early and allows for corrective measures to be implemented promptly.
- Ensuring Compliance: The governance board also plays a crucial role in ensuring that all automation efforts comply with relevant laws and regulations. This includes, but is not limited to, data privacy and labor laws. Their oversight can help prevent potential legal issues and maintain the organization’s reputation. It’s an essential aspect of risk management within the automation process.
- Evaluating Impact: Lastly, the governance board should take on the responsibility of assessing the impact of automation on various aspects of the organization. This involves evaluating improvements in productivity, gauging employee satisfaction, and quantifying cost savings. These assessments can help determine the overall effectiveness of the automation initiatives and provide valuable insights that can be used in planning and implementing future projects. This process of evaluation and learning is crucial for continuous improvement in the automation journey.
Conclusion
Human Resources (HR) automation is undeniably a powerful tool that holds the potential to revolutionize HR functions and significantly enhance overall organizational performance. The success of HR automation is hinged on the careful balance of automation with the critical aspect of its impact on the employee experience. This means that the automation process should enhance, not hinder, the employee experience.
Moreover, ensuring that processes are fit for automation is another pivotal factor. This involves a careful review and assessment of current processes to identify those that would benefit most from automation.
In the same vein, anticipating and taking action to balance employee skills in an automated environment is essential. This means reskilling or upskilling employees to ensure they remain valuable in an increasingly automated workplace.
Establishing a governance board is another key step. This board will oversee the implementation of the automation initiatives, ensuring that they are aligned with the organization’s overall strategic goals.
Additionally, the integration of automation with existing systems in the organization is a crucial step. This integration should be seamless to ensure the full functionality and effectiveness of the automation processes.
Cybersecurity should also be a top priority. With increased automation comes increased digital data, which could be vulnerable to cyber threats. Thus, securing this data should be a key consideration in the automation process.
Furthermore, measuring the Return on Investment (ROI) of the automation initiatives is essential to assess their effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
As the HR landscape continues to evolve, embracing automation strategically will be the key to staying competitive in the ever-changing business environment. Not only will it streamline processes, but it will also foster a positive and more efficient workplace environment, yielding lasting benefits for the organization.