Process mining bridges the gap between traditional business process management and data science. As businesses increasingly rely on digital systems, these systems leave behind event logs — timestamps, activity records, and data traces — that capture operational workflows in detail. Process mining analyses this data to provide deep insights into how processes are executed. Traditional business process analysis often relies on subjective methods like interviews and workshops, which provide incomplete pictures and don’t scale well for large organizations. Process mining offers a solution to this by using real-time data to visualize and enhance business operations.
In the digital age, the importance of understanding and optimizing processes is paramount. Companies must continuously improve efficiency, comply with regulations, and ensure quality while maintaining agility. Process mining is a game-changing tool that offers visibility, helping organizations to make data-driven improvements. It plays a pivotal role in the shift toward automation and digital transformation, helping businesses not only understand their current processes but also reimagine them for the future.
What is Process Mining?
Process mining uses event log data to derive insights into business processes. It operates by tracking the steps of each business task as recorded in IT systems such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) or CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software. The purpose is to uncover inefficiencies, hidden bottlenecks, and deviations from the intended process. Unlike traditional business process management, which often involves qualitative inputs from employees and managers, process mining leverages raw data to build an objective and accurate model of business operations.
One of the primary distinctions of process mining is its ability to derive process models directly from event logs, eliminating the need for preconceived models or manual intervention. There are different approaches and algorithms used for mining processes, with the goal of discovering, conformance checking, and enhancing business processes.
For instance, in the manufacturing industry, process mining helps to streamline production workflows by identifying bottlenecks that lead to delays. In healthcare, it helps to optimize patient flow and reduce waiting times. Process mining has gained traction in various industries that need to adapt their processes based on accurate data.
Why is Process Mining Important?
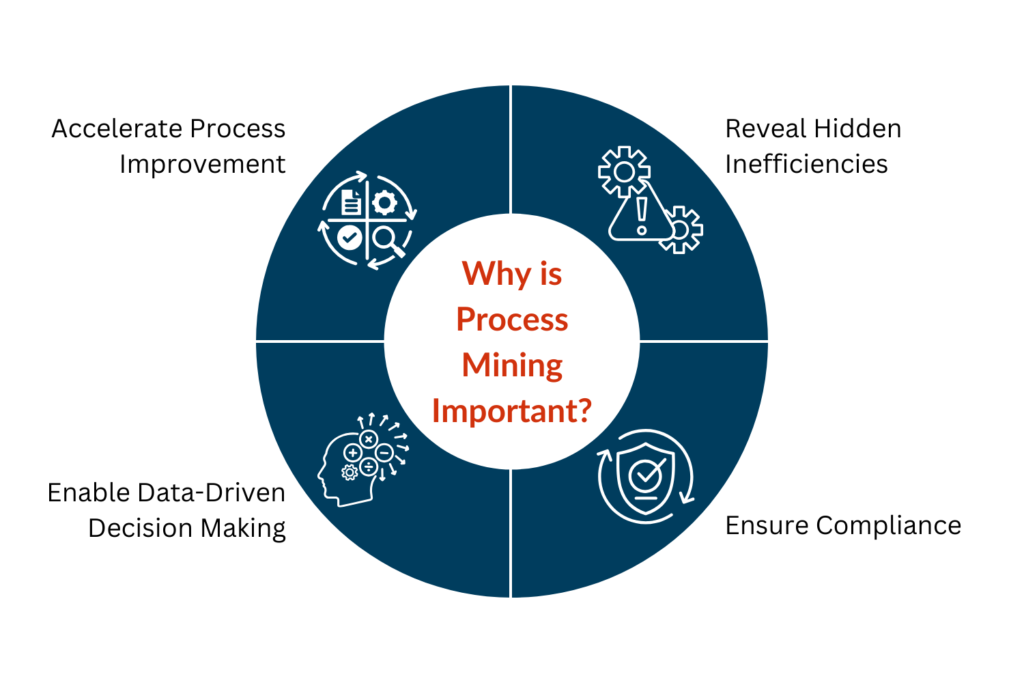
The importance of process mining lies in its ability to:
- Reveal Hidden Inefficiencies: Business processes can often be complex and layered, and inefficiencies can arise without being obvious to management. Process mining uncovers these inefficiencies by analysing every step of the process in detail.
- Ensure Compliance: With increasing regulatory requirements, especially in sectors like finance and healthcare, ensuring that processes conform to legal standards is critical. Process mining compares actual performance with prescribed models, identifying deviations that could indicate non-compliance.
- Enable Data-Driven Decision Making: Decisions based on subjective assessments can lead to errors. Process mining allows leaders to base their decisions on objective data derived from IT systems, minimizing risks and improving outcomes.
- Accelerate Process Improvement: By identifying bottlenecks, delays, and inefficiencies in real-time, organizations can take swift action to improve processes and thus reduce costs while increasing throughput.
A survey by Deloitte found that organizations using process mining have achieved a 30% reduction in process inefficiencies. This highlights how powerful it can be as a tool for operational improvement.
Lifecycle of Process Mining
The lifecycle of process mining includes several stages that work together to provide actionable insights:
- Event Log Extraction: This is the first step where event logs are gathered from IT systems. These logs are data points that record each step in the business process — for instance, when an invoice is created, approved, and paid.
- Process Discovery: Once the event logs are collected, process discovery algorithms are applied to visualize the entire workflow. This provides a model of the actual process based on how it’s performed in practice.
- Conformance Checking: Here, the discovered model is compared with the existing process model (if one exists). The aim is to identify any deviations from the intended process, which is crucial for compliance.
- Process Enhancement: Based on the findings from conformance checking, the model is refined, and processes are reengineered or optimized.
Process mining tools, such as Celonis and Disco, automate much of this lifecycle, making it easier for businesses to conduct continuous improvement without manually reviewing process performance.
The Four Types of Process Mining
Process mining is classified into four key types:
1. Process Discovery
Process discovery focuses on building a process model from scratch using event logs without relying on any existing process models. This is particularly useful when no formal process has been documented, but data is available from operational systems. The goal is to visualize what is happening in practice, which often reveals surprising deviations or inefficiencies.
2. Conformance Checking
Conformance checking involves comparing the discovered process model with an existing, theoretical model to check for deviations. This is particularly useful for audits and compliance-related tasks where processes must adhere to specific rules or regulations. The key is to ensure that the process is being executed as planned.
3. Process Reengineering (Enhancement)
After conducting process discovery and conformance checking, the next step is often process enhancement. This type of mining focuses on improving the existing process model by identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and deviations that hinder optimal performance. The insights gained from this analysis allow companies to reengineer their workflows to be more efficient.
4. Operational Support
Operational support refers to real-time insights that process mining tools provide to help businesses make immediate decisions to influence ongoing processes. Rather than reengineering the entire process, operational support helps tweak ongoing activities based on live data. For example, it can be used to prevent potential delays or adjust workloads.
How Process Mining Works
At its core, process mining works by analysing event logs generated by IT systems during the execution of business tasks. These logs are the digital traces left by tasks such as logging into systems, processing orders, or completing an approval workflow.
- Data Collection: The process begins with extracting event logs from IT systems. These logs are often stored in enterprise software like SAP, Oracle, or Microsoft Dynamics, capturing each step of the business processes.
- Event Log Analysis: Specialized algorithms then analyse the event logs to identify sequences of activities. The goal here is to construct a process model that accurately represents the flow of operations.
- Process Visualization: Once the analysis is complete, the process is visualized in the form of flowcharts, which provide a clear representation of how tasks move through the organization. These visualizations help to identify bottlenecks, deviations, and inefficiencies.
- Model Comparison and Optimization: The discovered model is compared with existing process models, and the differences are analysed to find areas for optimization or reengineering.
The entire process is data-driven and removes much of the guesswork traditionally involved in process improvement. Process mining tools enable continuous monitoring and real-time adjustments, providing a dynamic view of business operations.
Applications of Process Mining
Process mining has versatile applications across multiple industries:
- Manufacturing: By analysing the sequence of production events, manufacturers can optimize production lines, reduce waste, and improve throughput. It is especially useful for identifying machine downtimes or delays in supply chains.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, process mining can streamline patient care workflows, reduce wait times, and ensure compliance with healthcare regulations. Hospitals can use it to optimize resource allocation and ensure smoother patient journeys.
- Financial Services: Process mining helps banks and financial institutions improve their customer service processes, ensuring quicker responses and lower operational costs. It can also detect compliance issues and prevent fraud by analysing deviations in standard procedures.
- Supply Chain and Logistics: Logistics companies use process mining to improve supply chain efficiency by visualizing the flow of goods from supplier to customer. This helps in reducing delivery times and operational costs.
Benefits of Process Mining
- Increased Transparency: Process mining offers a data-driven view of operations, making processes visible that might otherwise be obscured by complexity.
- Reduced Costs: By identifying and eliminating inefficiencies, process mining helps organizations cut down operational costs.
- Improved Compliance: Process mining ensures that processes conform to internal and external standards, reducing the risk of compliance failures and penalties.
- Faster Process Improvements: The ability to monitor processes in real-time allows organizations to implement improvements swiftly, minimizing downtime and resource wastage.
- Enhanced Decision Making: Leaders can make informed, data-driven decisions that are based on accurate process data, improving the overall performance of the organization.
Challenges and Limitations in Process Mining
While process mining has proven its effectiveness, it comes with its challenges:
- Data Quality and Availability: Incomplete or poor-quality data can skew results, leading to incorrect process models. Ensuring clean, consistent data is critical for successful process mining.
- Concept Drift: As processes evolve, maintaining an accurate process model can be difficult. Changes in processes during analysis can lead to outdated or irrelevant models.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Older IT systems may not easily provide the event log data required for process mining. In large organizations with complex infrastructures, legacy systems pose integration challenges, requiring additional effort to extract and format data in a way that’s useful for analysis. Ensuring that the process mining tool is compatible with these systems, or using middleware to facilitate data extraction, can help address this issue.
- Complexity in Large Organizations: The volume of data in large organizations can create challenges in managing and interpreting process mining results. As processes become more complex, so too does the task of ensuring accuracy and extracting meaningful insights. Advanced process mining techniques, such as multi-level process mining, can help manage this complexity by breaking down processes into more manageable components.
- Resistance to Change: As with any process improvement initiative, organizations may face resistance from employees. Process mining often uncovers inefficiencies and areas for optimization, leading to changes in workflows or responsibilities. Employees accustomed to existing processes may resist these changes, which can slow down the implementation of new, optimized processes. Clear communication about the benefits of process mining, along with proper change management strategies, can mitigate this resistance.
Future Trends in Process Mining
The future of process mining is exciting, with several trends poised to transform the way organizations use this technology:
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms into process mining is one of the most significant trends. AI can predict potential process inefficiencies before they occur, enabling businesses to take preventive action. Machine learning can also help in developing more accurate process models by continuously learning from new data. This leads to smarter, more autonomous process optimization.
- Real-Time Process Mining: Real-time process mining enables organizations to monitor their processes as they happen, offering instant insights into performance. This helps businesses make immediate adjustments and respond to deviations on the fly. Industries like manufacturing and logistics, which require fast decision-making, are expected to benefit most from real-time process mining.
- Task Mining Integration: While process mining focuses on events captured in digital systems, it often misses manual tasks that aren’t logged by IT systems. Task mining aims to address this gap by capturing user-level actions, such as tasks performed on a computer, that are typically outside the scope of process mining. By combining task mining with process mining, organizations can achieve a more comprehensive understanding of their workflows.
- Increased Focus on Customer Experience: Process mining will increasingly be used to enhance customer experience by aligning internal processes with customer interactions. By analyzing event data related to customer journeys, companies can identify pain points and inefficiencies that negatively affect customer satisfaction. This customer-centric application of process mining is particularly relevant in industries such as retail and financial services.
- Cloud-Based Process Mining Solutions: As more businesses move their operations to the cloud, process mining vendors are increasingly offering cloud-based solutions. These platforms provide scalable, on-demand process mining capabilities that reduce the need for on-premise infrastructure and allow for seamless integration with other cloud-based systems. This trend is expected to grow, particularly among SMEs looking for affordable process mining tools.
Conclusion
Process mining is transforming how organizations optimize their operations by providing a clear, data-driven view of workflows. From discovering inefficiencies and ensuring compliance to enabling real-time decision-making, process mining offers a host of benefits across industries. However, as with any technology, it comes with challenges, particularly around data quality, integration, and complexity.
Looking ahead, the integration of AI, real-time capabilities, and task mining will further enhance the power of process mining. By adopting these advancements, organizations can stay ahead of the competition, reduce costs, and deliver better services to their customers. As the field continues to evolve, process mining will play a crucial role in driving continuous improvement and innovation across industries.